Vous avez besoin de retoucher vos photos de façon professionnelle mais vous ne voulez pas dépenser de grosses sommes pour des logiciels payants comme Photoshop ?
Pas de panique, il existe de nombreuses alternatives gratuites qui vous permettront de modifier et d’éditer vos images à votre guise sans sortir le porte-monnaie. D’ailleurs, n’hésitez pas à consulter notre sélection de sites de photos gratuites et libres de droit.
Découvrez maintenant notre classement des 15 meilleurs logiciels de retouche photo gratuits.
Les outils de cet article ont été sélectionnés par notre équipe et ne sont pas sponsorisés. Découvrez comment sponsoriser votre outil.
Trouvez un Graphiste pour votre projet
Graphiste.com est la meilleure plateforme de mise en relation pour trouver un graphiste freelance rapidement. Déposez gratuitement votre projet (création de logo, retouche photo, photographie de produit ou encore webdesign) sur la plateforme.
Nous communiquerons votre projet à nos 10 000 graphistes freelances et vous recevrez une quinzaine de devis en quelques minutes. Vous pourrez ensuite discuter avec les graphistes et sélectionner l’un d’entre eux (sans obligation).
Les logiciels de retouche photo gratuits
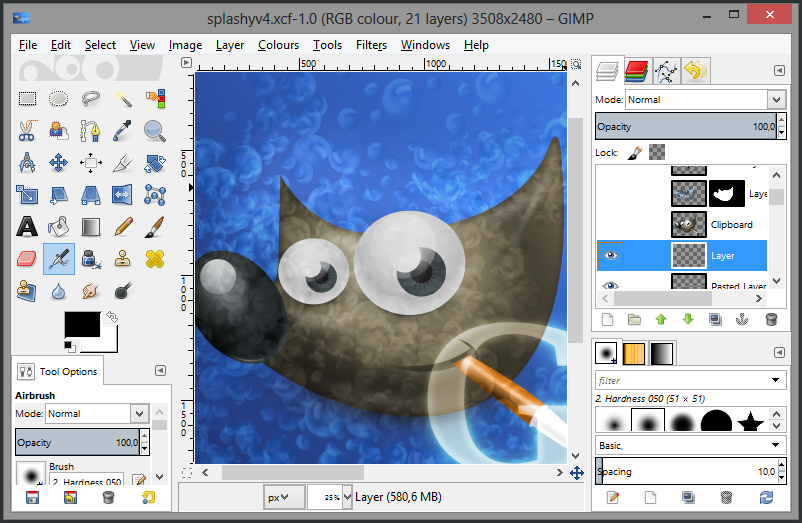
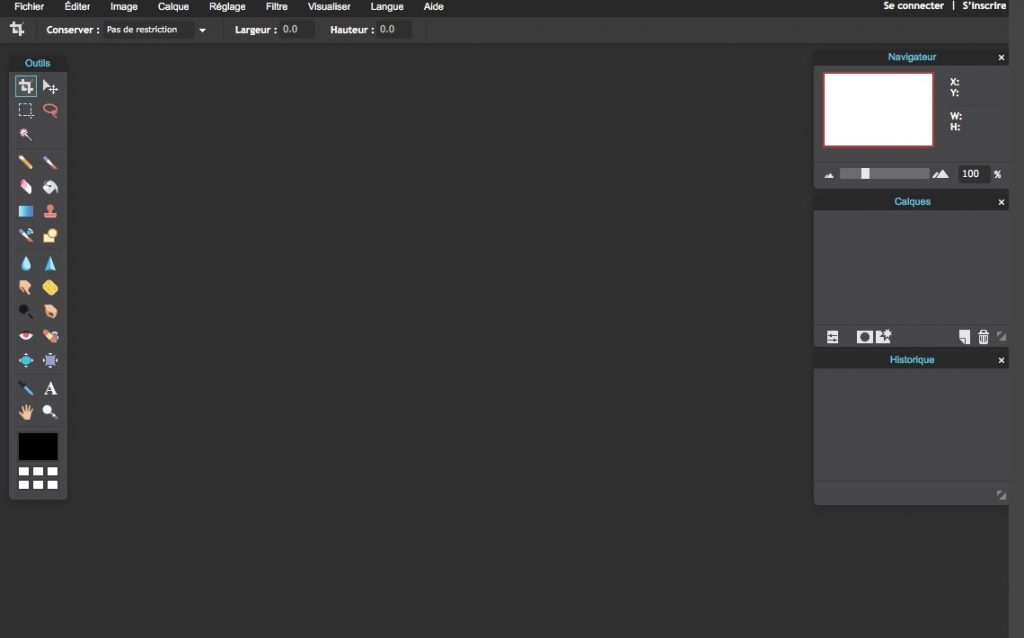
GIMP, l’incontournable
GIMP est un incontournable des outils de retouche photo gratuits, et il est certainement le plus complet de tous.
En contrepartie, il n’est pas le plus simple d’accès pour les non-initiés, mais il bénéficie d’une documentation complète en français pour vous aider.
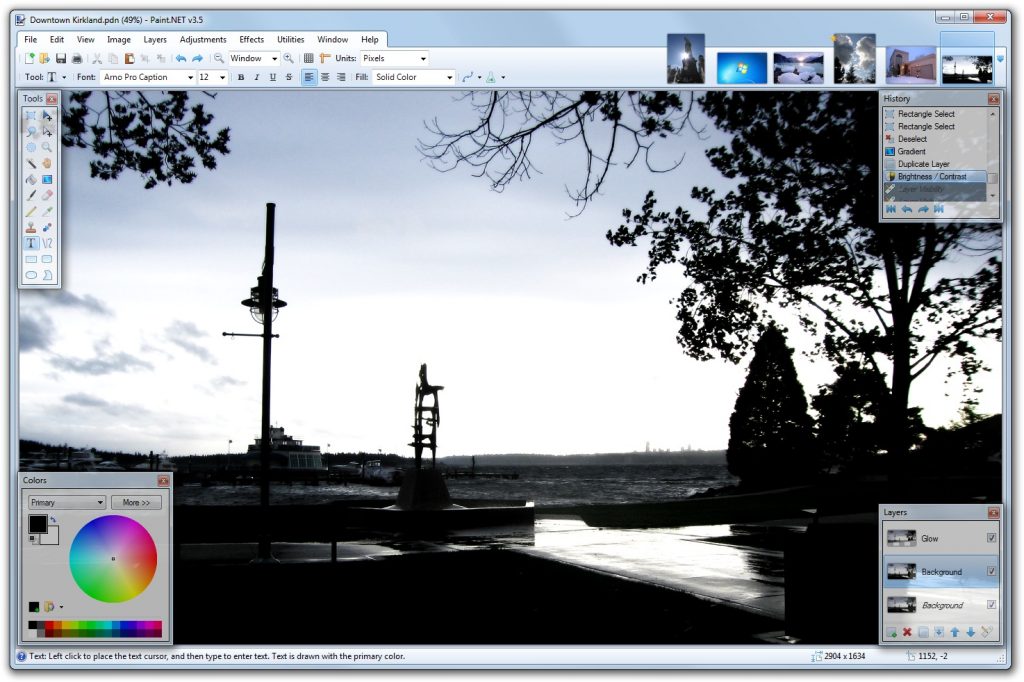
Paint.net, le logiciel de retouche photo gratuit Windows
Paint.net ne paye peut-être pas de mine, mais c’est un logiciel de retouche photo gratuit et complet tout en étant épuré.
Conçu à l’origine pour remplacer le fameux Paint de Microsoft, cet outil Windows a largement dépassé le précédent.
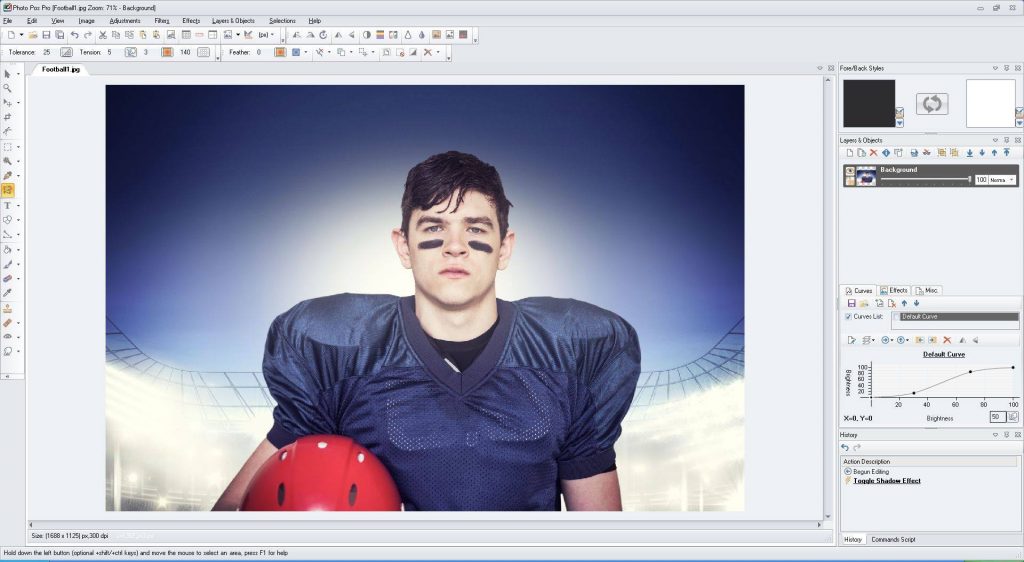
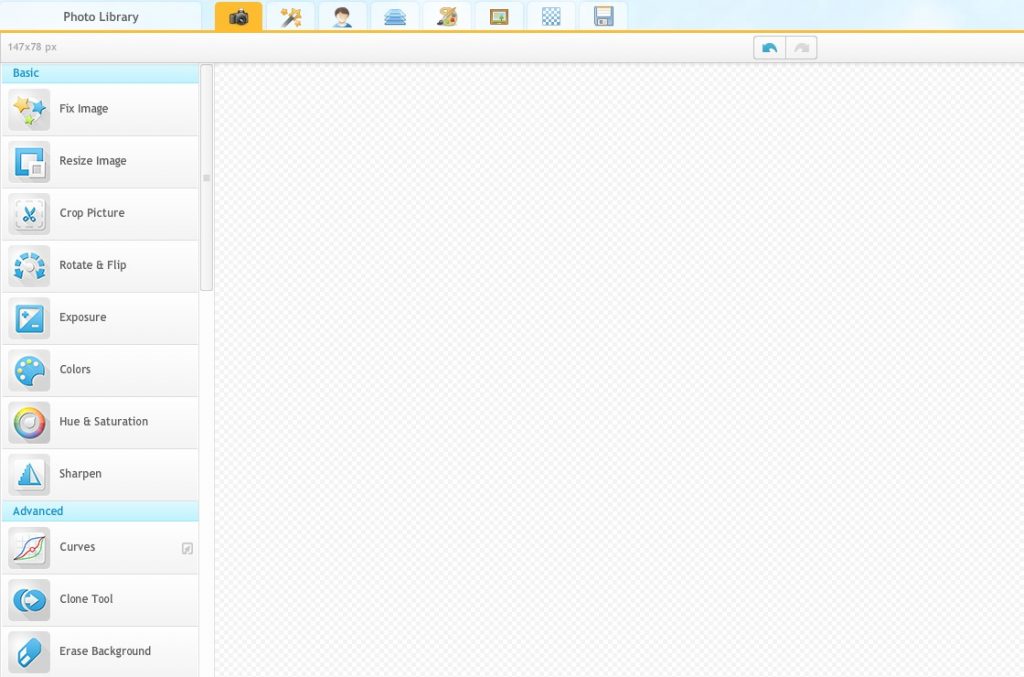
Photo Pos Pro, pour les débutants
Photo Pos Pro est un très bon logiciel de retouche photo gratuit pour Windows. Plus clair et accessible que GIMP, l’outil est notamment doté d’un mode “novice” permettant de simplifier l’édition.
En contrepartie, Photo Pos Pro connaît certaines limitations mais il reste amplement suffisant pour retoucher vos photos à votre guise.
PhotoScape X, un logiciel de retouche photo complet
Photoscape X est un logiciel de retouche photo gratuit, complet et performant, malgré son interface inhabituelle.
Il combine en fait une multitude d’outils vous permettant de modifier et de manipuler vos images comme bon vous semble, mais aussi de fusionner plusieurs images en une seule ou encore de créer des GIFs animés. Un véritable couteau suisse.
Successeur du logiciel Windows Photoscape, Photoscape X est supporté sur Windows 10 et Mac. Si vous disposez d’une version Windows antérieure, sachez que Photoscape est toujours disponible.
ON1 Effects 10 Free, pour ajouter des filtres photos en un clic
ON1 Effects 10 Free est une version gratuite (et donc limitée) d’un logiciel plus complet. Cela ne l’empêche pas de valoir le détour.
Son principal atout, c’est de permettre d’appliquer des filtres à certaines zones d’une image seulement (et pas à la photo entière). Cela vous laisse de nombreuses possibilités pour effectuer des retouches originales et uniques.
PhotoDiva, le logiciel de retouche de visages
PhotoDiva est LE logiciel gratuit pour la retouche photo de visages et corps. Disponible sur Windows, cet outil vous permettra de gommer toutes les imperfections physiques. Effacez les rides, ajoutez du maquillage, remodelez les corps, et changez la couleur des cheveux et des yeux en quelques clics depuis son interface intuitive.
Les outils de retouche photo en ligne gratuits
Besoin de rapidement créer, modifier ou optimiser un visuel pour votre site internet ? Envie de concevoir une image percutante pour vos réseaux sociaux ? Les plateformes en ligne gratuites sont idéales pour réaliser facilement quelques retouches sur vos photos rapidement.
Adobe Express, le petit frère gratuit d’Adobe Photoshop
Comme son nom l’indique, Adobe Express est une version light et online du fameux logiciel créatif. Il existe même en application pour iOS, Android et Windows Phone.
Ne vous inquiétez pas, il n’est pas nécessaire de maîtriser la suite Adobe pour pouvoir l’utiliser. Très dépouillé, il convient pour des retouches basiques, mais parfois nécessaires. Vous pourrez aisément recadrer une photo, jouer sur la luminosité et les contrastes, créer des effets d’ombre, supprimer l’effet « yeux rouges » ou ajouter des bordures.
SumoPaint, pour les plus confirmés
Dans le monde des logiciels de retouche photo en ligne, SumoPaint est sans doute l’un des plus poussés.
Se présentant comme une sorte de version “light” de Photoshop, SumoPaint plaira aux habitués de l’édition d’images qui veulent avoir accès à des fonctionnalités avancées sans débourser un centime.
Pixlr, une interface moderne pour retoucher vos photos
Pixlr est un outil de retouche photo en ligne qui dispose de toutes les fonctions de base dont vous avez besoin pour modifier vos images, sans avoir à télécharger quoi que ce soit.
Son interface simple et agréable rend Pixlr compréhensible et accessible à tous, même s’il ne possède pas certaines fonctionnalités plus approfondies.
iPiccy, la plateforme personnalisable
iPiccy est un outil de retouche photo en ligne riche et complet sans pour autant être indigeste.
Vous y trouverez un degré de personnalisation élevé sans pour autant vous y perdre. Un bon compromis pour ceux qui cherchent un logiciel assez poussé mais accessible.
Be Funky, pour créer des effets artistiques sur vos photos
Voici encore un outil de retouche photo au nom très évocateur. Be Funky vous permet de créer des effets artistiques sur vos visuels, en quelques clics. Vous transformez n’importe quelle photo en œuvre artistique. Ajoutez un effet gouache, sculpté, cartoon, encré, pointillé… pour rendre votre cliché unique !
Cet outil vous aide aussi à réaliser des collages à partager sur vos réseaux sociaux ou avec vos amis.
Enfin, Be Funky vous propose un mode « Concepteur ». Celui-ci vous permet de créer rapidement des flyers, brochures, cartes de visite, invitations, menus…
Attention toutefois : anciennement gratuit, Be Funky limite désormais l’accès à certaines fonctionnalités.
Editor.pho.to, pour s’amuser
Très complet, Editor Pho.to vous propose de nombreuses fonctionnalités pour retoucher vos images.
Pour vos portraits, l’outil présente des filtres bluffants qui corrigent toutes les imperfections : rides, boutons, yeux rouges, teint terne… Il peut même raviver la couleur des yeux, appliquer du maquillage supplémentaire et blanchir les dents.
Grâce à Editor Pho.to, vous aurez aussi la possibilité d’appliquer des effets amusants et, par exemple, de transformer votre image en couverture de magazine, cadre, photo ancienne, billet de banque, tête de mort, etc.
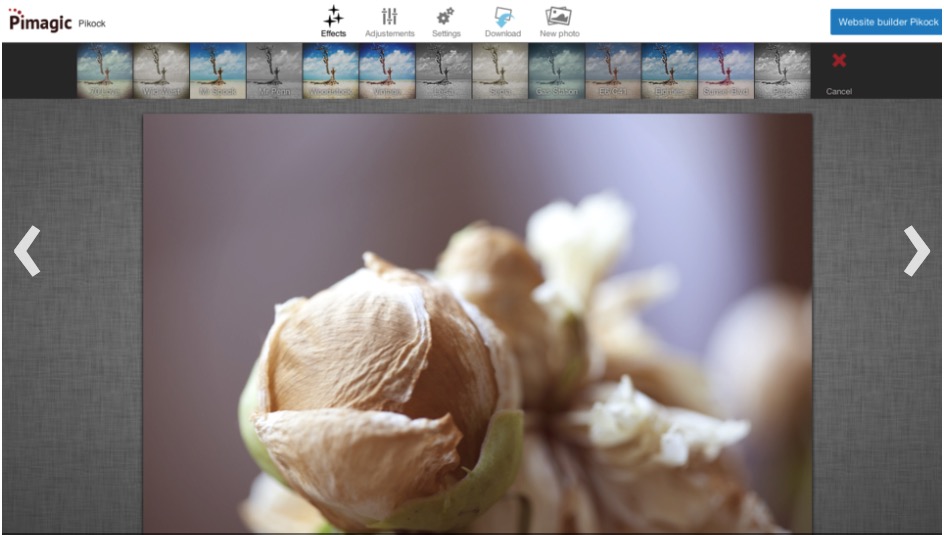
Pimagic, les basiques de la retouche photo
Dans une interface simplifiée, Pimagic vous offre les fonctions de base de la retouche photo : ajustement de la luminosité, des contrastes et des couleurs, ajout de filtres, recadrage, rotation…
Cet outil est pratique si vous souhaitez rapidement modifier ou optimiser un cliché. Notez que Pimagic est uniquement compatible avec les navigateurs suivants : Chrome 11+, Firefox 12+ et Safari 5.3+.
Lunapic, pour ajouter du texte facilement sur vos photos
Le design du site Lunapic est démodé, mais ses fonctionnalités s’inscrivent dans l’air du temps !
Vous pourrez, à partir d’une photo hébergée sur la toile, sur vos réseaux sociaux ou sur votre ordinateur, appliquer rapidement des effets. Vous aurez aussi la possibilité d’ajouter rapidement du texte, des icônes, des drapeaux, etc.
Lunapic vous permet également d’élaborer des gifs, des collages, des vidéos ou des animations.
Les logiciels de retouche photos gratuits sur mobile
Tous les logiciels gratuits présentés ci-dessus sont accessibles sur ordinateur, mais qu’en est-il du mobile ?
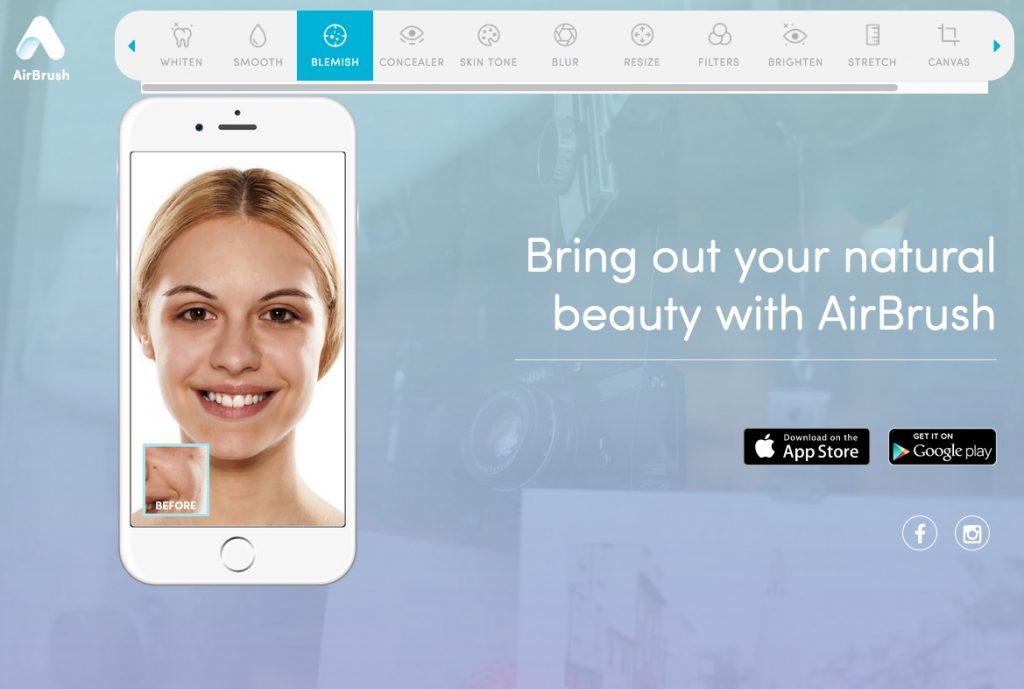
AirBrush, l’application pour magnifier les visages
AirBrush est une application mobile de retouche photo dont les effets et filtres se focalisent essentiellement sur les visages et la peau. Idéal pour retoucher votre dernier selfie en un rien de temps directement sur votre smartphone.
AirBrush est disponible sur Android et iOS.
Notre astuce pour retoucher vos photos
Avec ces 15 logiciels gratuits, vous pourrez retoucher toutes vos photos sans vous ruiner.
Il ne vous reste plus qu’à les tester pour créer des visuels professionnels et percutants, à utiliser sur votre site, dans vos articles de blog ou sur vos réseaux sociaux !
Bien sûr, pour une retouche d’image de qualité professionnel, vous pouvez aussi faire appel à un graphiste sur Graphiste.com.
| 🥇 Premier | Adobe Express |
|---|---|
| 🥈 Deuxième | Gimp |
| 🥉 Troisième | PhotoScape X |
| 🏅 Quatrième | PhotoDiva |